
We are currently bringing forth International Conference on Reproductive Health and Infertility (Reproductive Medicine 2023) which is going to be held during August 28-29, 2023 at London, UK with focusing on the theme “Frontiers in improving the chances of fertility and reproductive health”.
Reproductive health Conferences | Reproductive Health 2023 | London | UK

International Conference on Reproductive Health and Infertility

International Conference on Reproductive Health and Infertility
Theme: Frontiers in improving the chances of Fertility and Reproductive Health
Reproductive Medicine 2023
Welcome to the International Conference on Reproductive Health and Infertility (Reproductive Health 2023) taking place on August 28-29, 2023 in London, UK. This year's event will focus on exploring the latest developments and Frontiers in improving the chances of Fertility and Reproductive Health.
At Reproductive Health 2023, attendees will have the opportunity to participate in a range of thought-provoking presentations, workshops, and discussions led by leading experts in the field. The conference will provide a platform for attendees to exchange ideas and best practices, learn about the latest advances in reproductive health, and network with peers from around the world.
In addition to the educational opportunities, Reproductive Health 2023 will feature a robust exhibit hall showcasing the latest products and services in the field. With a range of exhibitors on hand, attendees will have the chance to explore new products, meet with representatives, and find out how they can improve their own practices.
Whether you are a researcher, clinician, or industry professional, Reproductive Health 2023 is the perfect opportunity to advance your knowledge and network with others in the field. We look forward to welcoming you to London this August for what promises to be an unforgettable event.
Target Audience:
The target audience for Reproductive Health 2023 includes but is not limited to the following:
- Reproductive health experts
- Obstetricians and gynecologists
- Fertility specialists
- Reproductive endocrinologists
- Reproductive scientists
- Andrologists
- Infertility counselors
- Embryologists
- Nurse practitioners
- Physician assistants
- Industry professionals
- Researchers in reproductive health and fertility
- Students and trainees in the field
This conference is designed for individuals who are passionate about advancing their knowledge in the field of reproductive medicine and improving the chances of fertility and reproductive health.
Why to Attend???
There are several compelling reasons to attend the Reproductive Health 2023 conference:
- Stay Current: Stay ahead of the curve by learning about the latest advances in the field of reproductive health and fertility.
- Networking Opportunities: Meet and connect with leading experts, researchers, and industry professionals from around the world.
- Inspiring Presentations: Attend inspiring presentations, workshops, and discussions led by renowned experts in the field.
- Hands-On Learning: Participate in hands-on learning opportunities, such as workshops and practical sessions.
- Exhibition Hall: Explore the latest products and services from top companies in the field of reproductive medicine and fertility.
- Enhance Your Skills: Expand your knowledge, improve your skills, and take your career to the next level.
- Discover New Innovations: Discover new products and services that can help improve your practice or research.
- Career Advancement: Attend this conference to grow professionally and increase your chances of career advancement.
- Collaboration: Collaborate and exchange ideas with peers, experts, and researchers in the field.
- Experience London: Take advantage of this opportunity to visit London and explore this vibrant city while you attend this conference.
Overall, Reproductive Health 2023 is a must-attend event for anyone who wants to advance their knowledge, network with peers, and explore new products and services in the field of reproductive medicine and fertility.
Scope and Importance:
The scope and importance of the Reproductive Health 2023 conference are significant in the field of reproductive medicine and fertility. The conference will cover a wide range of topics that are crucial to the advancement of this field, including:
- Fertility and reproductive health: The conference will highlight the latest advances and best practices in fertility and reproductive health.
- New technologies: Attendees will learn about the latest technologies and innovations that are improving the chances of fertility and reproductive health.
- Clinical practices: The conference will feature presentations and discussions on the latest clinical practices in reproductive medicine and fertility.
- Research and development: Attendees will learn about the latest research and developments in the field of reproductive medicine and fertility, including advances in genetic engineering, stem cell research, and assisted reproductive technologies.
- Collaboration and networking: The conference provides an ideal platform for attendees to exchange ideas, network with peers, and form partnerships with industry professionals.
- Career advancement: The conference provides attendees with opportunities to expand their knowledge, improve their skills, and grow professionally.
The importance of this conference lies in its ability to bring together a diverse group of experts, researchers, and industry professionals to discuss and share the latest advancements and best practices in the field of reproductive medicine and fertility. This exchange of ideas and knowledge will help to advance the field and improve the chances of fertility and reproductive health for people around the world.
Sessions and Tracks
Track 1: Infertility & Related Disorders: Diagnosis, Treatment & Management
The most common disorders that leads to infertility include uterine fibroids, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), primary ovarian insufficiency and endometriosis. Uterine fibroids, or leiomyoma are the common non-cancerous tumor cells grow in the walls of the uterus and is more common in women with child bearing age (25-44). Uterine fibroids lead to abnormal bleeding from uterus and sever pain. Uterine fibres present in uterus leads to infertility by hindering the pregnancy process. Hysterectomy is the only curing option of fibroids. Endometriosis is another condition in which there are abnormal growth of cells inside the uterus and these cells grow outside of uterus resulting pain and leads to infertility. In case of Primary ovarian insufficiency (POI), the ovaries stop functioning normally before the age of 40. It hinders the ovulation process and leads to infertility.
Track 2: Reproductive Health: Diseases & Disorders
Reproductive health is important to take steps to protect reproductive system from infections and injury, and prevent problems—including some long-term health problems. Taking care of yourself and making healthy choices can help protect you and your loved ones. Reproductive health, consequently, suggests that people are able to have a liable, satisfying and safer sex life and that they have the ability to reproduce and the liberty to choose if, when and how frequently to do so. One clarification of this suggests that men and women should to be informed of and to have contact to safe, effective, reasonable and acceptable methods of birth control; also contact to appropriate health care facilities of sexual, reproductive medicine and application of health training programs to pressure the importance of women to go safely through pregnancy and childbirth could offer couples with the best chance of having a healthy baby. On the other hand, individuals do face variations in reproductive health services.
Track 3: Reproductive Medicine
Reproductive medicine is a department of medicine that deals with prevention, diagnosis and management of reproductive problems Reproductive medicine goals include improving or maintaining reproductive health and allowing people to have children at a time of their choosing. It is form on knowledge of reproductive anatomy, physiology, and endocrinology, and incorporates applicable aspects of molecular biology, biochemistry and pathology.
Reproductive medicine addresses matters of sexual education, adolescence, family planning, birth control, infertility, reproductive system disease and erotic dysfunction. In women, reproductive medicine also covers menstruation, pregnancy and menopause, as well as gynaecologic complication that affect fertility.
The field work together with and connections mainly with reproductive endocrinology and infertility, sexual medicine and anthology, but also to some grade with gynaecology, obstetrics, urology, genitourinary medicine, therapeutic endocrinology, paediatric endocrinology, genetics, and psychiatry.
Track 4: Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome is caused by a hormonal secretion imbalance. Elevated levels of endocrine internal production within the duct gland result in an excess release of endocrine into the bloodstream, resulting in the impact of the ovaries. As the name suggests, PCOS is caused by the formation of a variety of cysts within the ovary. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a condition in which females have elevated levels of androgenic hormone (male hormone), which is characterized by irregular catamenial cycles, acne, significant periods, and excess body and facial hair.
PCOS is a condition characterized by internal abnormalities of the ovaries. 8-15% of women with procreative age square measure are significantly affected. Stein-Leventhal Syndrome is another name for it. Women in this condition have a higher risk of high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, and female internal reproductive organ cancer, which is known as (Endometrial Cancer). The majority of PCOS women have multiple cysts on their ovary.
Track 5: Gynecology & Obstetrics
Gynecology can be defined as the branch of medical science that deals with the health of the female reproductive systems (vagina, ovaries and uterus) and the breasts. This term also means, “The science of women” outside medicine. A gynecologist deals with various types of diseases which include Cancer and pre-cancerous diseases of reproductive organs, Amenorrhoea, Infertility, Dysmenorrhoea, Menorrhagia, Infections of the vagina, cervix and uterus, Premenstrual Syndrome, Prolapse of pelvic organs, and other vaginal diseases. All of the modern gynaecologists are also obstetrics as in many areas the specialities of both gynecology and obstetrics overlap.
Obstetrics on the other hand is the area of study which is mainly focused on pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period.
- Various gynaecological operations
- Parental Care
- Intercurrent diseases in pregnancy
- Induction and labour
- Pain management during childbirth
- Complications and emergencies
- Postnatal Care
Track 6: Pregnancy and Womens Health care
Pregnancy is normally isolated into three trimesters. The principal trimester is from week one through 12 and incorporates origination. Origination is the point at which the sperm prepares the egg. The prepared egg then goes down the fallopian tube and appends to within the uterus, where it starts to shape the baby and placenta. The primary trimester conveys the most noteworthy danger of unnatural birth cycle (common passing of developing life or fetus). The second trimester is from week 13 through 28. Around the center of the second trimester, development of the baby might be felt. At 28 weeks, more than 90% of children can make due outside of the uterus if gave astounding medicinal care. The third trimester is from 29 weeks through 40 weeks
Track 7: Urologic and Gynecologic Disorders
Endometriosis, interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome, incontinence, urinary tract infections, and uterine fibroids are some of the primary issues classified as urologic and gynaecologic disorders.
Patients will usually be assessed using a combination of history taking, examination (including pelvic examination and assessment of prolapse using validated systems such as the Pelvic Organ Prolapse Quantification [POP-Q] system) and assessment of quality of life impact using validated questionnaires, including the assessment of sexual function using Pelvic Organ Prolapse/Incontinence Sexual Questionnaire IUGA- Revised [PISQ-IR].
Track 8: Women Reproductive Cancers
Reproductive cancers are growths that happen in the Reproductive organs. They can influence both men and woman. In woman’s, these are cancers in the breast, cervix, uterus, vulva, endometrium or ovaries. In men, Reproductive growths can be found in the prostate, gonads and penis. Gynecologic cancer is a growth that begins in woman conceptive organs. The five gynecologic growths start in better places inside a woman’s pelvis, which is the region beneath the stomach and in the middle of the hip bones.
Track 9: Reproductive Toxicology
Reproductive toxicity is a hazard related with some chemical substances, that they will affect in some way with usual reproduction; such materials are called reprotoxic. It comprises adverse properties on sexual role and fertility in mature males and women, as well as developmental toxicity in the offspring. It is normal to take a practical meaning, including a number of different properties which are unconnected to each other excepting in their consequence of lowered effective fertility. The Worldwide Harmonized System of Organization and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) separates reproductive harmfulness from germ cell mutagenicity and carcinogenicity, even still both these hazards may also affect fertility. Some well-known group of substances which are poisonous for reproduction are teratogens – constituents which cause birth deficiencies – of which(S)-thalidomide is possibly the most infamous. Another group of constituents which has conventional much attention (and some controversy) as possibly toxic for reproduction are the so-called endocrine disruptors. Though, many constituents which are toxic for reproduction do not fall into any of these groups: lead compounds, for sample, are careful to be toxic for reproduction assumed their opposing effects on the normal intelligent and psychomotor growth of human babies and children.
Track 10: Sexually Transmitted Diseases/Infections
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are caused by infections that are passed from one person to another during sexual contact.
These infections often do not cause any symptoms. Medically, infections are only called diseases when they cause symptoms. That is why STDs are also called "sexually transmitted infections." But it’s very common for people to use the terms "sexually transmitted diseases" or "STDs," even when there are no signs of disease. There are many kinds of sexually transmitted diseases and infections.
Track 11: Maternal and Perinatal Health
Maternal nutrition has a major role in fetal growth and development. Maternal nutrition not only refers to the nutritional needs of women during the antenatal and postnatal period (i.e., when they are pregnant and breastfeeding) but also to the pre-conceptual period (i.e., adolescence). Any kind of alterations in fetal nutrition or endocrine status may result in developmental adaptations that permanently change the structure, metabolism and physiology of the offspring, thereby predisposing individuals to metabolic, endocrine, and cardiovascular diseases in adult life.
Track 12: Sexual and Reproductive Health and Rights
Sexual and reproductive health and rights or SRHR is the concept of human rights applied to sexuality and reproduction. It is a combination of four fields that in some contexts are more or less distinct from each other, but less so or not at all in other contexts. These four fields are sexual health, sexual rights, reproductive health and reproductive rights. In the concept of SRHR, these four fields are treated as separate but inherently intertwined.
Track 13: Male Reproductive Cancers and Infertility
Reproductive dysfunction associated with the male gender signify a serious health concern, their incidence has notably risen over the past years. Prior to treatment, testicular or prostate cancer sufferers often show terrible semen characteristics similar to infertile patients. The diagnosis of infertility is implied when a couple has continuous unprotected intercourse for at least one year without being able to conceive. Male reproductive dysfunction has received substantial interest from academics and researchers over the past few decades. It is now broadly time-honored that copy in men might also be compromised by way of underlying tumors special to the male gender, such as testicular and prostate cancer.
Track 14: Reproductive Endocrinology
Reproductive endocrinology and infertility is a precise subspecialty of obstetrics and gynaecology that Pullman’s physicians in reproductive medicine make a speech hormonal functioning as it affects to reproduction as well as the matter of infertility. Although most REI specialists mainly focus on the treatment of infertility, reproductive endocrinologists are trained to also estimate and treat hormonal dysfunctions in females and males outside infertility. Reproductive endocrinologists have specialty working out in obstetrics and gynaecology before they undergo sub-specialty training (fellowship) in REI.
Track 15: Family Planning
Women access to family planning facilities are empowered to make lifesaving choosing such as delaying motherhood, spacing their pregnancies and avoiding accidental pregnancies and abortions. Females who make these choosing and plan their relations prevent as various as one in each three maternal deaths and more than two million new-born and adolescent deaths. Yet, many more lives could be saved.
Family Planning Postpartum women need to know the benefits of control and spacing their following pregnancy for their own and their baby’s well-being, and that it is probable to develop pregnant earlier the arrival of menses. If they are not breastfeeding, their fertility may return by six weeks after childbirth. A female’s fertility can arrival within two weeks after an abortion or failure. So, it is important that women who receive post abortion care leave hospitals with modern contraceptive methods and Family Planning information. By providing Family Planning counselling and appropriate contraceptive systems at the time females accept post abortion care facilities, providers can help females avoid the dangerous cycle of unwanted pregnancy and abortion.
Track 16: Reproductive Technology
Reproductive technology encompasses all current and anticipated uses of technology in human and animal reproduction, including assisted reproductive technology, contraception and others. It is also referred to as assisted reproductive technology, where it involves a range of devices and procedures that enable the achievement of safe, improved and healthier reproduction. Although not for all men and women, for a range of married couples the ability to have children is vital. But thanks to technology, infertile couples were given options that would allow them to conceive children.
Track 17: Menopause
The term menopause refers to the end of a woman's menstrual cycle. It's diagnosed after a 12-month period without a menstrual period. Menopause is a common occurrence in women's reproductive systems. The supply of mature eggs in a woman's ovaries diminishes and ovulation becomes irregular. At the same time, the production of estrogen and progesterone decreases. There is a variety of effective therapy available, ranging from lifestyle changes to hormone medication. Women who smoke and are underweight tend to have an earlier menopause, while women who are overweight often have a later menopause.
Track 18: Midwifery
Midwifery is a medical health profession that focuses on nursing or aiding pregnant women before and after birth, as well as women's reproductive and sexual health throughout their lives. Obstetrics is another name for it. It involves a decrease in the use of epidurals, as well as fewer episiotomies and instrument deliveries. There are increased chances of being cared for in labour by a midwife known to the childbearing woman, as well as increased chances of having a spontaneous vaginal birth and a chance of losing the baby before 24 weeks gestation period, with no apparent differences in the risk of losing the baby after 24 weeks or overall. A midwife's duties and responsibilities include assessing and monitoring pregnant women, doing screening tests, and providing antenatal care in hospitals, homes, and GP practises. Good interpersonal skills are essential for a midwife. It entails being able to interact and communicate with people in a variety of scenarios. It works with patients, their families, and other medical professionals. The primary distinction between doctors and midwives is that midwives manage uncomplicated, normal, and low-risk pregnancy cases, whereas doctors address difficult cases.
Track 19: Fertility Awareness
Fertility recognition refers to a set of practices used to determine the fertile and infertile phases of a woman's menstrual cycle. Fertility consciousness methods may additionally be used to avoid pregnancy, to attain pregnancy, or as a way to screen gynecological health. Methods of figuring out infertile days have been regarded due to the fact that antiquity, but scientific know-how received at some point of the previous century has elevated the quantity and range of methods. Various techniques can be used and the Symptothermal technique has accomplished a success rates over 99% if used properly.
Track 20: Breast Cancer during Pregnancy
During pregnancy your breasts change in readiness for breast feeding. The breast tissue becomes denser. This can make it more difficult to find changes in the breast that are due to cancer. The most common symptom of breast cancer is a lump. If you have a change that doesn’t go away after 2 to 4 weeks tell your doctor or midwife. It is also because the cancer can be difficult to diagnose because of the changes in the breast tissue. If the biopsy shows that you have cancer you may then have other tests to check the size of your cancer. Deciding which treatment to have and what that will mean for you and your developing baby can be very difficult. Doctors advise that your treatment should be as close as possible to what someone who isn’t pregnant would have. And whenever possible the treatment should not be delayed.
Track 21: Abortions & Women’s Health
Premature birth is the closure of pregnancy by expelling a baby or fetus before it can get by outside the uterus. A premature birth which happens suddenly is otherwise called an unsuccessful labor. A premature birth might be brought about intentionally and is then called an actuated fetus removal, or less much of the time, "incited unsuccessful labor".
Regularly regarded as essentially ladies' conceptive wellbeing, numerous gatherings contend for a more extensive definition relating to the general strength of ladies, better communicated as "The soundness of ladies".
Track 22: Reproductive Immunology
Reproductive immunology is a field of medicine that studies the interactions between the immune system and the reproductive system. The current area of ​​study in reproductive medicine is the role of the immune system in recurrent pregnancy loss and repeated IVF failures.
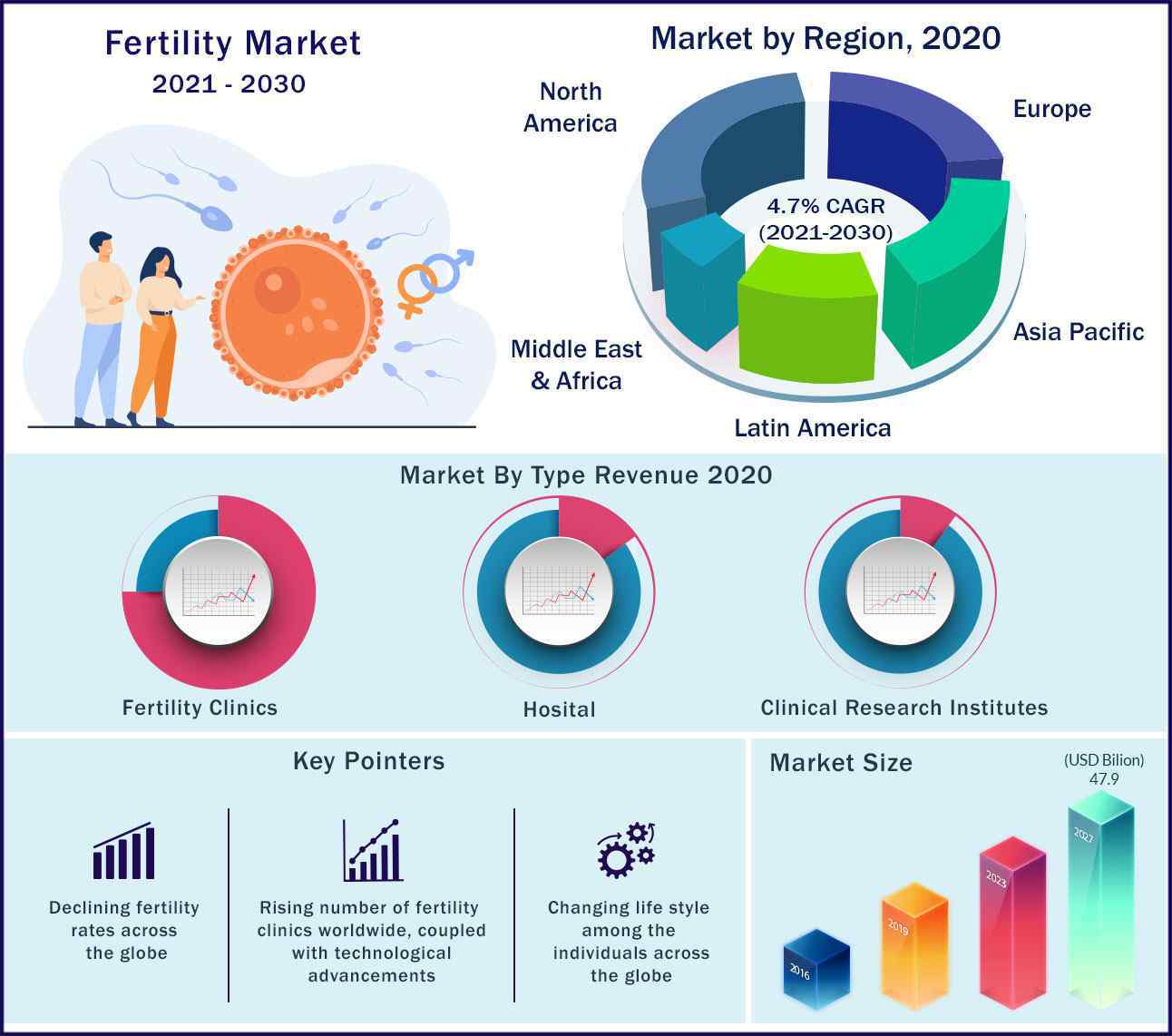
The global fertility market was valued at USD 26.88 billion in 2020 and projected to reach USD 45.40 billion by 2027, at a noteworthy CAGR of 4.7% during the forecast period 2021 to 2027. The growth is mainly due to the companies rearranging their operations and recovering from the COVID-19 impact, which had earlier led to restrictive containment measures involving social distancing, remote working, and the closure of commercial activities that resulted in operational challenges. The market is expected to reach $3.40 billion in 2026 at a CAGR of 3.9%.
Research & developments are continually increasing in the healthcare industry for the infertility treatment which is expected to boost target industry growth in the near future. In the developed countries such as U.S and Canada the healthcare treatment, service costs are relatively high owing to availability of advanced healthcare infrastructure. Due to the ongoing healthcare technology advancements highly sophisticated tools and apps are used every day, around the globe. However, the emerging economies across the globe such as India, China are offering huge opportunities to the key operating players in the target market. Further, advancements in the healthcare infrastructure, coupled with growing medical tourism because of less costs of treatments are major factors boosting growth opportunities in the emerging economies, worldwide. Growth in the number of same-sex parents as well as solitary women selecting to have children has been exponential. All these factors are expected to boost growth and demand patterns for the global fertility industry in future.
Vital influences accountable for market growth are:
- Declining fertility rates across the globe
- Rising number of fertility clinics worldwide, coupled with technological advancements
- Changing life style among the individuals across the globe
COVID-19 Impact on Global Fertility Market:
The outburst of COVID-19 has affected most of the world's main markets, with no exception being the fertility market. For example, pregnant women do not appear to be at a higher risk of serious illness, according to data released by the WHO. In fact, in pregnant and non-pregnant women of reproductive age, the WHO notes that there is currently no established difference between the clinical forms of COVID-19. However, there is no information available about the precise effect of COVID-19 on fertility and abortion. The American Society for Reproductive Medicine released a guidance paper on fertility care during the COVID-19 pandemic, after considering the evidence relevant to COVID-19, calling for the termination of new treatment cycles, the cancellation of all embryo transfers and the suspension of elective surgery in March 2020. COVID-19, however, is increasingly resolving the situation and most companies are beginning their facilities at maximum capacity.
Future of Global Fertility Market:
Major companies of the global industry including Cooper Surgical and Cook Group are pointing towards commercial growth by adopting strategies like mergers and acquisitions, heavy investments in the manufacturing facilities that are predictable to flourish the global market growth in next few years. This trend is probable to continue and will augment growth of the target industry in the near future. For instance, in 2018, Cooper Surgical a leading player in the global industry acquired fertility business of Life Global Group. This has increased chances of a healthy pregnancies.
Top companies contending in the Market:
- Boston IVF Fertility Clinic
- INVO Bioscience
- San Diego Fertility Center
- Celmatix
- FUJIFILM IRVINE SCIENTIFIC
- Carolinas Fertility Institute
- Progyny Inc.
- Cook Medical
- LifeGlobal Group (Cooper Surgical)
Key Market Developments:
- In year 2020, Invo Bioscience, Trading pvt ltd, and Medesole healthcare, leading players worldwide came in to an agreement in order to operate dedicated invocell fertility clinics in the India.
- In 2019, FUJIFILM Irvine Scientific a major player in the target industry introduced Vit Kit-NX for in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Conference Highlights
- Infertility & Related Disorders: Diagnosis, Treatment & Management
- Reproductive Health: Diseases & Disorders
- Reproductive Medicine
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
- Gynecology & Obstetrics
- Pregnancy and Womens Health care
- Urologic and Gynecologic Disorders
- Women Reproductive Cancers
- Reproductive Toxicology
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases/Infections
- Maternal and Perinatal Health
- Sexual and Reproductive Health and Rights
- Male Reproductive Cancers and Infertility
- Reproductive Endocrinology
- Family Planning
- Reproductive Technology
- Menopause
- Midwifery
- Fertility Awareness
- Breast Cancer during Pregnancy
- Abortions & Women’s Health
- Reproductive Immunology
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | August 28-29, 2023 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Reproductive System & Sexual Disorders: Current Research
- Gynecology & Obstetrics
- Andrology & Gynecology: Current Research
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by

